- Home
- About Us
- Students
- Academics
-
Faculty
- Electrical Engineering
- Automation
- Computer Science & Engineering
- Electronic Engineering
- Instrument Science and Engineering
- Micro-Nano Electronics
- School of Software
- Academy of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering
- School of Cyber Security
- Electrical and Electronic Experimental Teaching Center
- Center for Advanced Electronic Materials and Devices
- Cooperative Medianet Innovation Center
- Alumni
-
Positions
-
Forum
News
- · Shanghai Jiao Tong University professors Lian Yong and Wang Guoxing's team have made remarkable progress in the field of high-efficiency pulse neural network accelerator chips.
- · AI + Urban Science research by AI Institute was selected as cover story in Nature Computational Science!
- · The first time in Asia! IPADS's Microkernel Operating System Research Wins the Best Paper Award at SOSP 2023
- · Delegation from the Institution of Engineering and Technology Visits the School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering for Journal Collaboration
- · Associate professor Liangjun Lu and research fellow Jiangbing Du from Shanghai Jiao Tong University made important advancements on large capacity and low power consumption data transmission
One Master Graduate Student of SEIEE won the Student Paper Award
Recently,2022 SPIE Medical Imaging was successfully held in San Diego, CA, United States. TANG Yaoqi, master graduate student supervised by Prof. LING Yuye,won the winner of Image Processing Student Paper Award, for the paper titled, “Multi-scale Sparse Representation-Based Shadow Inpainting for Retinal OCT Images”. This work is the result of a collaboration between Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai General Hospital and The University of Alabama. Shanghai Jiao Tong University is the institution of the first author.
SPIE Medical Imaging is the leading conference where the latest information in digital pathology; tomography; image processing, perception, registration, informatics, and segmentation; computer-aided diagnosis; and ultrasound is presented.

Currently, the number of people with vision loss is increasing worldwide. The most effective way to prevent vision loss is early diagnosis and early intervention. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive, high-resolution imaging modality, which has been widely used in clinical settings for diagnosing ophthalmic disease to generate retinal images. However, there will be artifacts including the shadows that are caused by scattering from the superficial retinal vessels, which would decrease the accuracy of automated segmentation algorithms and cause errors in clinical diagnosis. Therefore, an accurate shadow inpainting algorithm that is applicable for suppressing such artifacts in retinal OCT images is very important for the diagnosis of ophthalmic diseases.
For shadow inpainting, traditional methods generate less satisfactory outcomes when dealing with larger missing regions, while deep learning methods typically need a long computational time for network training in addition to the high demand on the size of datasets. To address these challenges, this study proposes a multi-scale shadow inpainting framework for OCT images by synergically applying sparse representation and deep learning to utilize multi-scale information. This method consists of three procedures: preprocessing, image inpainting and postprocessing. An input retinal OCT image that contains shadowed regions of different widths is first flattened and fed to an A-line-based shadow detection algorithm. Shadows with smaller width are directly inpainted in sparse representation module, while shadows with larger width are first downsampled. The inpainted strips will be upsampled via super-resolution network to restore the image quality and later be regularized by a regularizing module to integrate complementary feature information.
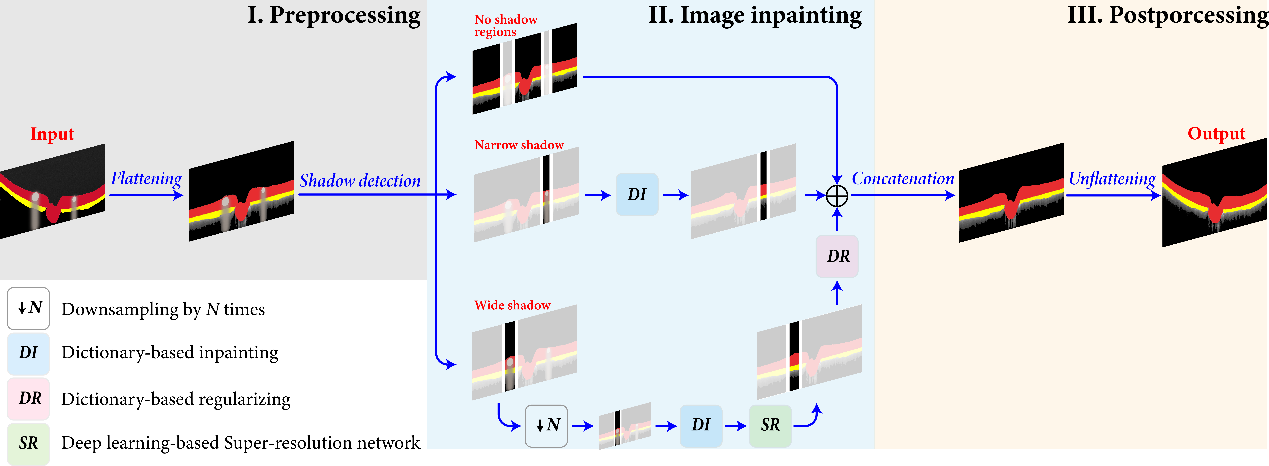
Figure 1:The framework of the method
With a relatively smaller dataset and training time, this method achieves expected results on both synthetic shadows and real shadows, which could improve the performance of subsequent segmentation algorithms and is suitable for real-time clinical medical applications.
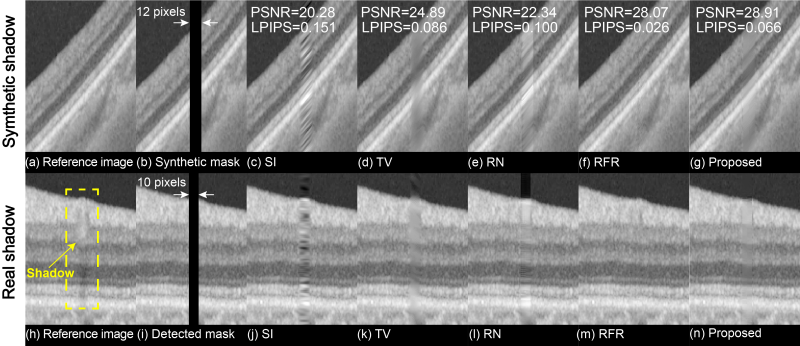
Figure 2: Comparison between different methods for inpainting synthetic shadows and real shadows
-
Students
-
Faculty/Staff
-
Alumni
-
Vistors
-
Quick Links
